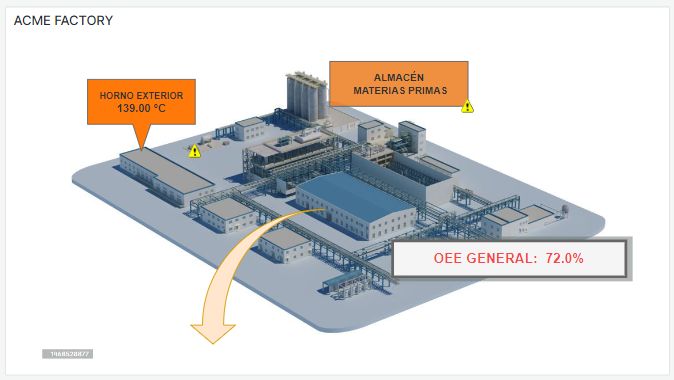
Dashboards are for the summer
August 13, 2019
Advantages of using a SaaS cloud monitoring system
September 12, 2019

Comparison MQTT vs OPC-UA
In today's blog we will compare two of the most popular protocols in the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) environment: MQTT and OPC-UA, to try to shed some light on their differences and uses. Let's start by looking at a small summary of the main characteristics of these two well-known message exchange protocols, with MQTT being one of the most popular in the IoT world and, for some years now, OPC UA in industrial environments.
The MQTT protocol to follow the subscription publishing model defines two entities in the network: the broker, also called the server, and the clients. The clients are any device that is going to interact with the broker, either publishing messages or subscribing to a topic. Topics are the routes where messages are published within a broker. This helps us to have the information sorted and better manage the messages.
Messages follow this format:
Company/oven1/temperature
By defining themselves with this structure, topics allow us to use wildcards to increase their flexibility, allowing us to subscribe to multiple topics.
# - wildcard multilevel
+ - wildcard singlelevel
Let's suppose that we now have the following topics:
company/oven2/temperature
company/oven/humidity
MQTT
MQTT (Message Queue Telemetry Transport) is a lightweight message protocol that is based on a subscription-publishing model, in which publishers send messages to a server and this is who forwards messages to subscribers avoiding point-to-point connections between subscribers and publishers, this allows subscribers not need to know who provides the information to which is subscribed. MQTT is designed to be implemented in low-resource devices, in low-bandwidth networks and high latency.The MQTT protocol to follow the subscription publishing model defines two entities in the network: the broker, also called the server, and the clients. The clients are any device that is going to interact with the broker, either publishing messages or subscribing to a topic. Topics are the routes where messages are published within a broker. This helps us to have the information sorted and better manage the messages.
Messages follow this format:
Company/oven1/temperature
By defining themselves with this structure, topics allow us to use wildcards to increase their flexibility, allowing us to subscribe to multiple topics.
# - wildcard multilevel
+ - wildcard singlelevel
Let's suppose that we now have the following topics:
company/oven2/temperature
company/oven/humidity
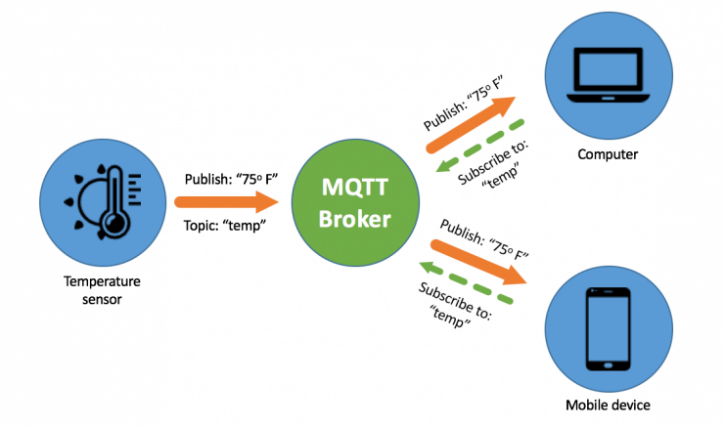
Using wildcards we could subscribe to all the messages within "company/oven1/" selecting the topic "company/oven1/#", if now we want to receive only all the temperatures of the ovens, we would only have to subscribe to the topic "company/*/temperature". In the broker are published all the messages within their respective topics, the broker is responsible for receiving the messages and forwarding them to customers subscribed to those topics.
The client-server connection for sending the messages is made via a TCP connection or an encrypted TLS connection in case secure messages need to be sent.
The message can be in any data format for the payload, such as JSON, XML, encrypted binary or Base64. This gives a lot of flexibility to the protocol, but the target client must be able to analyze the type of load.
The protocol supports sending messages with quality of service, leaving three different levels to choose from:
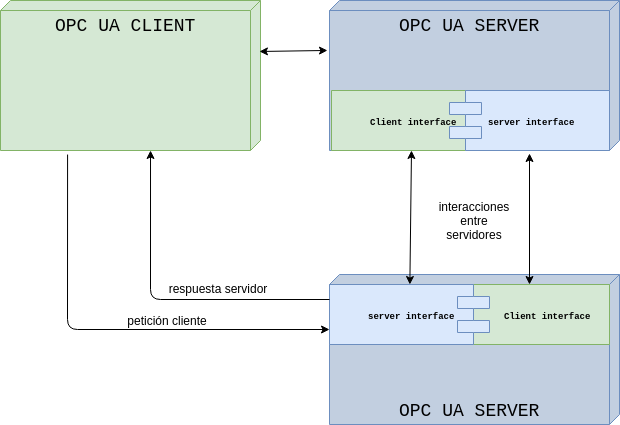
OPC UA servers define the services they can provide to clients, an object model that can be dynamically discovered by clients and a data model following the data-types defined in the protocol itself.
A client can communicate with one or several servers, a server in the same way can communicate with several clients. Servers can act as clients for communication with other servers.
The client-server connection for sending the messages is made via a TCP connection or an encrypted TLS connection in case secure messages need to be sent.
The message can be in any data format for the payload, such as JSON, XML, encrypted binary or Base64. This gives a lot of flexibility to the protocol, but the target client must be able to analyze the type of load.
The protocol supports sending messages with quality of service, leaving three different levels to choose from:
- 0 without quality of service. The message is sent only once, in case the client is not available the message will be lost.
- 1 the message will be resent until it arrives at least once, this can lead to some duplication in the reception of the messages.
- 2 the message will reach the client only once.
OPC-UA
OPC UA (Open Platform Communications Unified Architecture)) is a platform-independent standard through which various types of systems and devices can communicate by sending request and response messages between clients and servers or similarly to MQTT via a subscription-publishing model.OPC UA servers define the services they can provide to clients, an object model that can be dynamically discovered by clients and a data model following the data-types defined in the protocol itself.
A client can communicate with one or several servers, a server in the same way can communicate with several clients. Servers can act as clients for communication with other servers.
OPC UA gives a consistent and integrated address space (AddressSpace) and service model. This allows a single server to integrate data, alarms and events into this address space and provide access to them using its integrated services that incorporate mechanisms for customers to detect and recover communication failures.
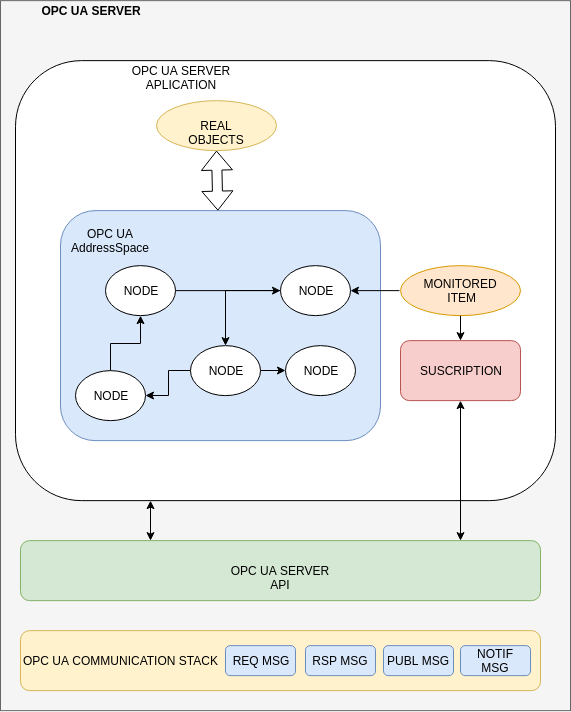
OPC UA provides security mechanisms for authentication of users, clients and servers, checking the integrity of communications and providing security at transport level by encrypting and signing messages.
OPC UA seeks to facilitate the way of operating between the devices of different manufacturers by establishing a common form of communication, this makes it especially useful in industrial environments where devices of different manufacturers can coexist, allowing the communication of all of them with a single client, or even between the devices themselves.
MQTT is a protocol where the data field coding and its content are specific to each application, therefore, it will be useful when the communication of messages is for a specific application developed for those data fields.
OPC UA (Unified Architecture) is a complete architecture where the communication protocol is only a part. An OPC UA application allows to see all network nodes, methods, data structures. The communication can be based both on a published subscription model and on the client server model where the server shows a group of services to access the nodes of the network making possible the reading, writing, calling methods of the servers, and so on.
Now let's give an example, such as the writing of a variable hosted in a PLC.
As we saw earlier, MQTT is designed to be lightweight and energy efficient. For that reason it does not have implemented the search of the topic nor of the broker where the message is published, this does that it is necessary that the client knows it beforehand. In the same way it does not have any mechanism implemented for the writing of the variable in the machine.
Therefore, for this implementation we will need a client program that is subscribed to the topic in the broker, this program must process the message published, access the PLC and write the variable.
This has several problems:
All these problems are solved with OPC UA. For the writing of a variable in an OPC UA server, it would be simply with a series of requests from the OPC client itself. The steps that the protocol would follow would be: open a secure channel, see the list of available endpoints, create the session, write the value of the variable, close the session and close the channel.
On the other hand, the bandwidth consumption of doing the writing, without counting the sending of the writing request, exceeds 600 Bytes when sending the variable to write using the MQTT protocol consumes about 17 Bytes.
The conclusion we reached is that each protocol must be used for what it was designed for. MQTT for devices with low resources, low bandwidth networks, high latency or in applications that require the flexibility of this protocol and OPC UA for industrial environments, since it seeks to unify the way of operating with different manufacturers of industrial devices being a complete solution that covers from the communication of the devices to their interoperability, in these environments the increase in bandwidth consumption is not so critical as not to compensate all the advantages that OPC UA brings us.
Muutech's Minerva platform, based on Zabbix and Grafana works with both protocols, so do not hesitate to contact us if you need a monitoring platform that combines the IoT world with the world of industrial and IT systems.
OPC UA seeks to facilitate the way of operating between the devices of different manufacturers by establishing a common form of communication, this makes it especially useful in industrial environments where devices of different manufacturers can coexist, allowing the communication of all of them with a single client, or even between the devices themselves.
COMPARISON
Currently, after seeing their main characteristics, we can affirm that making a comparison between these two protocols is not entirely fair.MQTT is a protocol where the data field coding and its content are specific to each application, therefore, it will be useful when the communication of messages is for a specific application developed for those data fields.
OPC UA (Unified Architecture) is a complete architecture where the communication protocol is only a part. An OPC UA application allows to see all network nodes, methods, data structures. The communication can be based both on a published subscription model and on the client server model where the server shows a group of services to access the nodes of the network making possible the reading, writing, calling methods of the servers, and so on.
Now let's give an example, such as the writing of a variable hosted in a PLC.
As we saw earlier, MQTT is designed to be lightweight and energy efficient. For that reason it does not have implemented the search of the topic nor of the broker where the message is published, this does that it is necessary that the client knows it beforehand. In the same way it does not have any mechanism implemented for the writing of the variable in the machine.
Therefore, for this implementation we will need a client program that is subscribed to the topic in the broker, this program must process the message published, access the PLC and write the variable.
This has several problems:
- Processing of the message, the published message does not have a specific format, therefore, the subscriber has to know the format in which he will receive the message.
- The writing of the data in the PLC varies depending on the manufacturer.
All these problems are solved with OPC UA. For the writing of a variable in an OPC UA server, it would be simply with a series of requests from the OPC client itself. The steps that the protocol would follow would be: open a secure channel, see the list of available endpoints, create the session, write the value of the variable, close the session and close the channel.
On the other hand, the bandwidth consumption of doing the writing, without counting the sending of the writing request, exceeds 600 Bytes when sending the variable to write using the MQTT protocol consumes about 17 Bytes.
The conclusion we reached is that each protocol must be used for what it was designed for. MQTT for devices with low resources, low bandwidth networks, high latency or in applications that require the flexibility of this protocol and OPC UA for industrial environments, since it seeks to unify the way of operating with different manufacturers of industrial devices being a complete solution that covers from the communication of the devices to their interoperability, in these environments the increase in bandwidth consumption is not so critical as not to compensate all the advantages that OPC UA brings us.
Muutech's Minerva platform, based on Zabbix and Grafana works with both protocols, so do not hesitate to contact us if you need a monitoring platform that combines the IoT world with the world of industrial and IT systems.

CTO & TECHNICAL DIRECTOR
Expert in industrial monitoring and data analytics.
We tell you how to improve decision-making and production efficiency in your plant, without wasting time generating reports. Your plant at a glance!
Subscribe to our Newsletter